Difference between revisions of "Format"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Format command is used to erase a device or hard disk partition. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It can be used from Workbench with it's user interface or alternatively as a command line program. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''WARNING: the Format process is a destructive operation and will erase data currently stored on the device or partition you are formatting. Ensure that any data you wish to keep is backed-up before starting the Format process.'' | ||
== Using Format == | == Using Format == | ||
Revision as of 12:03, 16 April 2016
Introduction
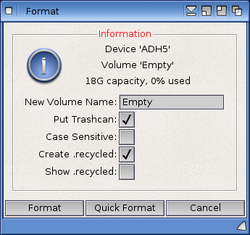
The Format command is used to erase a device or hard disk partition.
It can be used from Workbench with it's user interface or alternatively as a command line program.
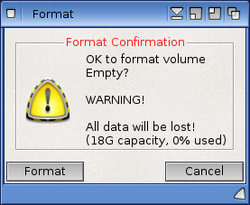
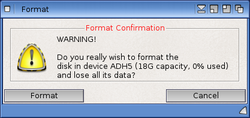
WARNING: the Format process is a destructive operation and will erase data currently stored on the device or partition you are formatting. Ensure that any data you wish to keep is backed-up before starting the Format process.
Using Format
Workbench
Format can be invoked from the Workbench by right clicking on a device and selecting the Format disk... option from the icons menu or it can be run directly from the System drawer by double clicking on it's icon. If you run it directly, the Format Select Device window will appear listing the available devices on the system.
Command Line
Alternatively Format command can be run directly from the CLI.
Shown below are the command line options that the Format command accepts in the CLI:
DEVICE=DRIVE/K/A,NAME/K/A,OFS/S,FFS/S,INTL=INTERNATIONAL/S, NOINTL=NOINTERNATIONAL/S,DIRCACHE/S,NODIRCACHE/S,LN=LONGNAME/S, NOICONS/S,QUICK/S,NOVERIFY/S,NOCONFIRM/S,MAXMEM/K/N,RETRY/K/N, LOGFILE/K,CS=CASESENSITIVE/S,NR=NORECYCLED/S,SR=SHOWRECYCLED/S